Jan 30, 2023The solubility product constant, Ksp K s p , is the equilibrium constant for a solid substance dissolving in an aqueous solution. It represents the level at which a solute dissolves in solution. The more soluble a substance is, the higher the Ksp K s p value it has. Consider the general dissolution reaction below (in aqueous solutions):
Solubility Curve Worksheet With Answers | Teaching chemistry, Chemistry education, Chemistry worksheets
Complete the following solubility constant expression for CaCO3.Ksp = This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts.

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
1,692 solutions Modern Chemistry 1st Edition • ISBN: 9780547586632 (1 more) Jerry L. Sarquis, Mickey Sarquis 2,184 solutions kg ? Determine the freezing point depression of a solution that contains 30.7 g glycerin (C H _8 O 3, molar mass = 92.09 g/mol) in 376 mL of water. Some possibly helpful constants for water are a) 0.887 °C b) 1.65 °C

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
SOLVED: The solubility product constant expression, Ksp, for Ag3PO4 can be written as , where x represents the molar solubility of Ag3PO4. a) Ksp = x^2 b) Ksp = 4x^3 c) Ksp = The solubility product constant expression for CaCO3 is Ksp = [Ca2+] [CO32-]. Since equal quantities of Ca2+ (aq) and CO32- (aq) are produced when CaCO3 dissolves, this expression reduces to 4.9 × 10-9 = x2, or 49 × 10-10 = x2. This can be solved directly by taking the square root of each side. Question

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Complete The Following Solubility Constant Expression For Caco3
The solubility product constant expression for CaCO3 is Ksp = [Ca2+] [CO32-]. Since equal quantities of Ca2+ (aq) and CO32- (aq) are produced when CaCO3 dissolves, this expression reduces to 4.9 × 10-9 = x2, or 49 × 10-10 = x2. This can be solved directly by taking the square root of each side. Question Question Transcribed Image Text: < = 2 = 3 Ksp = 0 = 4 = 5 = 6 Complete the following solubility constant expression for CaCO3. = 7 X 00 S 010 8 Expert Solution Trending now This is a popular solution! Step by step Solved in 3 steps See solution Check out a sample Q&A here Knowledge Booster Learn more about Chemical Equilibrium
SOLVED: Writing a solubility product (Ksp) expression. Complete the following solubility constant expression for Mg(OH)2.
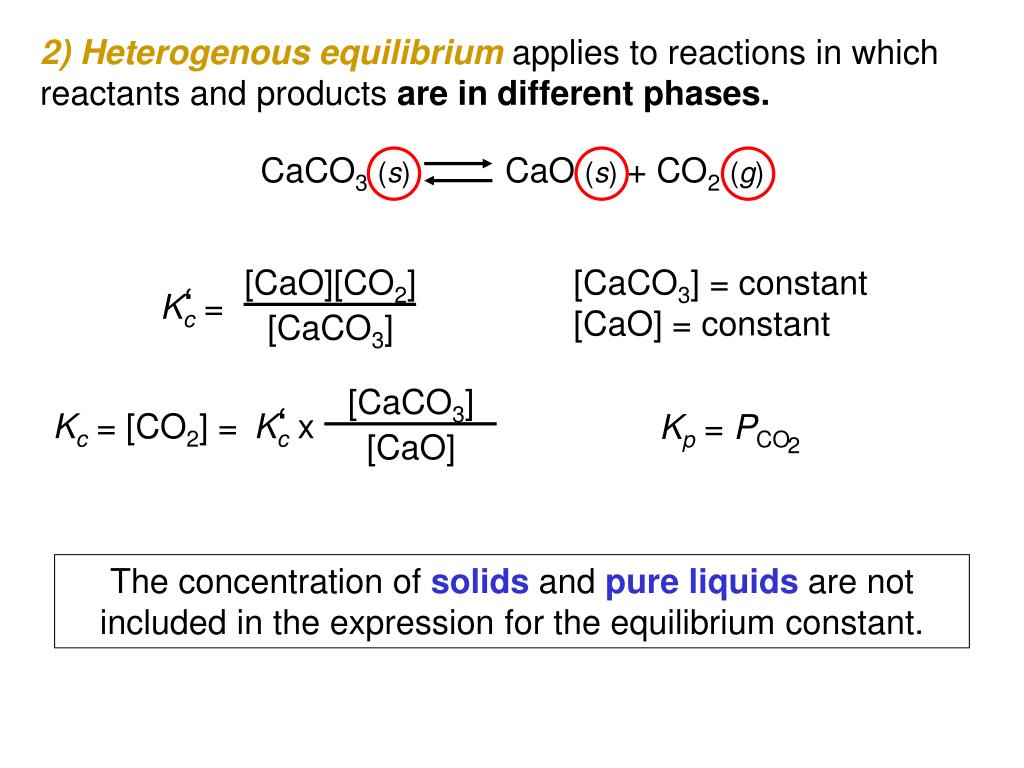
C. K sp = [CaCO3]/ [Ca2+] [CO32-] D. K sp = [Ca2+]2 [CO32-]2. CaCO3 is a product of the reaction and a solid. The reactants are Ca2+ and CO3 2-. We’re being asked to find the solubility constant Ksp for CaCO3. From my understanding, you’ll never include a solid or pure liquid in these formulas. So this allowed me to eliminate options A and C. PPT – Chemical Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:3973838
Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
The values of Ksp of CaCO3 and CaC2O4 are 4.7 x 10^-9 and 1.3 x 10^-9 respectively at 25°C. – Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community C. K sp = [CaCO3]/ [Ca2+] [CO32-] D. K sp = [Ca2+]2 [CO32-]2. CaCO3 is a product of the reaction and a solid. The reactants are Ca2+ and CO3 2-. We’re being asked to find the solubility constant Ksp for CaCO3. From my understanding, you’ll never include a solid or pure liquid in these formulas. So this allowed me to eliminate options A and C.
Source Image: sarthaks.com
Download Image
Solubility Curve Worksheet With Answers | Teaching chemistry, Chemistry education, Chemistry worksheets Jan 30, 2023The solubility product constant, Ksp K s p , is the equilibrium constant for a solid substance dissolving in an aqueous solution. It represents the level at which a solute dissolves in solution. The more soluble a substance is, the higher the Ksp K s p value it has. Consider the general dissolution reaction below (in aqueous solutions):

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
SOLVED: The solubility product constant expression, Ksp, for Ag3PO4 can be written as , where x represents the molar solubility of Ag3PO4. a) Ksp = x^2 b) Ksp = 4x^3 c) Ksp = 1,692 solutions Modern Chemistry 1st Edition • ISBN: 9780547586632 (1 more) Jerry L. Sarquis, Mickey Sarquis 2,184 solutions kg ? Determine the freezing point depression of a solution that contains 30.7 g glycerin (C H _8 O 3, molar mass = 92.09 g/mol) in 376 mL of water. Some possibly helpful constants for water are a) 0.887 °C b) 1.65 °C
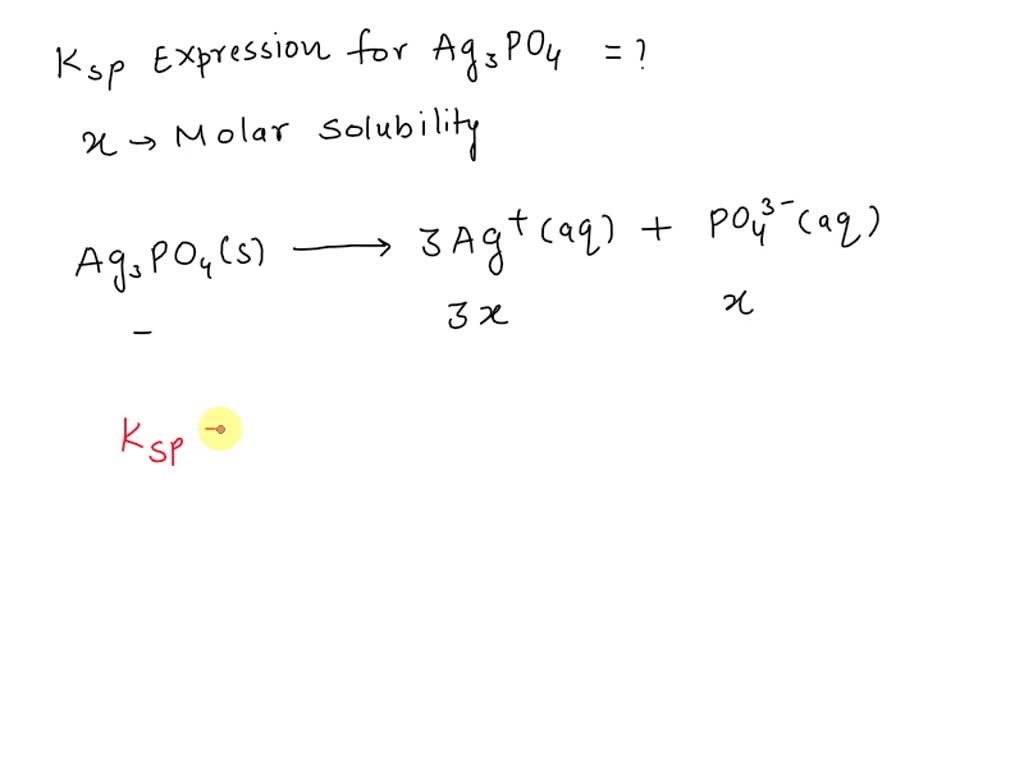
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Explain in detail 13 Equilibrium constant for the reaction, CaCO3 (s)⇋ CaO(s) + CO2(g), follows the equation – Chemistry – General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements – 12362573 | Meritnation.com CaCO 3 (s) + H 2 CO 3 (aq) ⇌ Ca 2+ (aq) + 2HCO 3- (aq) To dissolve calcium carbonate: Increase pressure or decrease temperature. Per the ideal gas law, this allows more CO 2 to enter the water. The extra CO 2 creates more H 2 CO 3. There is too much H 2 CO 3 for equilibrium.

Source Image: meritnation.com
Download Image
PPT – Chemical Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:2170056 The solubility product constant expression for CaCO3 is Ksp = [Ca2+] [CO32-]. Since equal quantities of Ca2+ (aq) and CO32- (aq) are produced when CaCO3 dissolves, this expression reduces to 4.9 × 10-9 = x2, or 49 × 10-10 = x2. This can be solved directly by taking the square root of each side. Question

Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
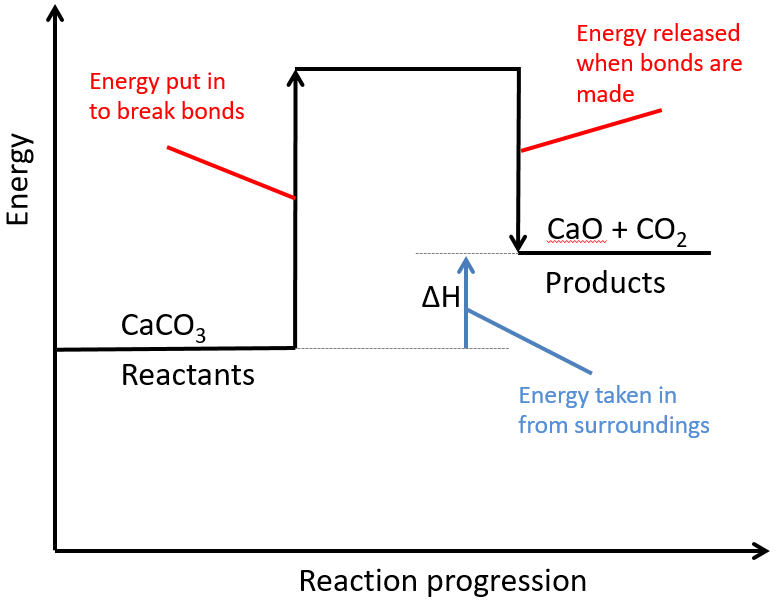
3:14 (Triple only) draw and explain reaction profile diagrams showing ΔH and activation energy – TutorMyself Chemistry Question Transcribed Image Text: < = 2 = 3 Ksp = 0 = 4 = 5 = 6 Complete the following solubility constant expression for CaCO3. = 7 X 00 S 010 8 Expert Solution Trending now This is a popular solution! Step by step Solved in 3 steps See solution Check out a sample Q&A here Knowledge Booster Learn more about Chemical Equilibrium
Source Image: tutormyself.com
Download Image
The values of Ksp of CaCO3 and CaC2O4 are 4.7 x 10^-9 and 1.3 x 10^-9 respectively at 25°C. – Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community
3:14 (Triple only) draw and explain reaction profile diagrams showing ΔH and activation energy – TutorMyself Chemistry Complete the following solubility constant expression for CaCO3.Ksp = This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts.
SOLVED: The solubility product constant expression, Ksp, for Ag3PO4 can be written as , where x represents the molar solubility of Ag3PO4. a) Ksp = x^2 b) Ksp = 4x^3 c) Ksp = PPT – Chemical Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:2170056 CaCO 3 (s) + H 2 CO 3 (aq) ⇌ Ca 2+ (aq) + 2HCO 3- (aq) To dissolve calcium carbonate: Increase pressure or decrease temperature. Per the ideal gas law, this allows more CO 2 to enter the water. The extra CO 2 creates more H 2 CO 3. There is too much H 2 CO 3 for equilibrium.