Expert Answer Transcribed image text: Match each characteristic to the appropriate chromatography technique.
Nontoxic ammunition: Challenges and perspectives for GSR identification – Carneiro – 2023 – WIREs Forensic Science – Wiley Online Library
Chromatography can be used to separate and identify the components in a mixture. Column chromatography (CC) – a column is packed with a solid and a solvent moves down the column. Gas chromatography (GC) – a column is packed with a solid or with a solid coated by a liquid, and a gas is passed through the column under pressure at high

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
There are many types of chromatography e.g., liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, affinity chromatography, but all of these employ the same basic principles. Chromatography is a separation technique that every organic chemist and biochemist is familiar with.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Application of a Target-Guided Data Processing Approach in Saturated Peak Correction of GC×GC Analysis | Analytical Chemistry
Aug 29, 2023Thin layer chromatography is done exactly as it says – using a thin, uniform layer of silica gel or alumina coated onto a piece of glass, metal or rigid plastic. The silica gel (or the alumina) is the stationary phase. The stationary phase for thin layer chromatography also often contains a substance which fluoresces in UV light – for reasons

Source Image: thermofisher.com
Download Image
Match Each Characteristic To The Appropriate Chromatography Technique
Aug 29, 2023Thin layer chromatography is done exactly as it says – using a thin, uniform layer of silica gel or alumina coated onto a piece of glass, metal or rigid plastic. The silica gel (or the alumina) is the stationary phase. The stationary phase for thin layer chromatography also often contains a substance which fluoresces in UV light – for reasons
Chromatography is based on the principle where molecules in mixture applied onto the surface or into the solid, and fluid stationary phase (stable phase) is separating from each other while moving with the aid of a mobile phase.
The Easy Way to Transfer Methods in Liquid Chromatography
Match each characteristic to the appropriate chromatography technique. The native protein, as seen after gel filtration chromatography, has a molecular mass of 140,000 Daltons. But denatured protein, as seen during SD-PAGE, reveals that the protein is comprised of four subunits: two 25,000-Dalton subunits and two subunits at 45,000 Daltons
Fully Conjugated Donor–Acceptor Covalent Organic Frameworks for Photocatalytic Oxidative Amine Coupling and Thioamide Cyclization | ACS Catalysis

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
7 Factors to Consider When Choosing an HPLC Detector | PerkinElmer Blog
Match each characteristic to the appropriate chromatography technique. The native protein, as seen after gel filtration chromatography, has a molecular mass of 140,000 Daltons. But denatured protein, as seen during SD-PAGE, reveals that the protein is comprised of four subunits: two 25,000-Dalton subunits and two subunits at 45,000 Daltons
Source Image: blog.perkinelmer.com
Download Image
Nontoxic ammunition: Challenges and perspectives for GSR identification – Carneiro – 2023 – WIREs Forensic Science – Wiley Online Library
Expert Answer Transcribed image text: Match each characteristic to the appropriate chromatography technique.

Source Image: wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Download Image
Application of a Target-Guided Data Processing Approach in Saturated Peak Correction of GC×GC Analysis | Analytical Chemistry
There are many types of chromatography e.g., liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, affinity chromatography, but all of these employ the same basic principles. Chromatography is a separation technique that every organic chemist and biochemist is familiar with.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Wholesale Affordable HPLC Peek Tubing for Accurate Results -uHPLCs
Aug 29, 2023Chromatography. Chromatography is a method by which a mixture is separated by distributing its components between two phases. The stationary phase remains fixed in place while the mobile phase carries the components of the mixture through the medium being used. The stationary phase acts as a constraint on many of the components in a mixture

Source Image: uhplcs.com
Download Image
UPLC for the Analysis of Synthetic Peptides and for the Development of Isolation Strategies | Waters
Aug 29, 2023Thin layer chromatography is done exactly as it says – using a thin, uniform layer of silica gel or alumina coated onto a piece of glass, metal or rigid plastic. The silica gel (or the alumina) is the stationary phase. The stationary phase for thin layer chromatography also often contains a substance which fluoresces in UV light – for reasons
Source Image: waters.com
Download Image
Fermentation | Free Full-Text | Valorization of Fermented Food Wastes and Byproducts: Bioactive and Valuable Compounds, Bioproduct Synthesis, and Applications
Chromatography is based on the principle where molecules in mixture applied onto the surface or into the solid, and fluid stationary phase (stable phase) is separating from each other while moving with the aid of a mobile phase.
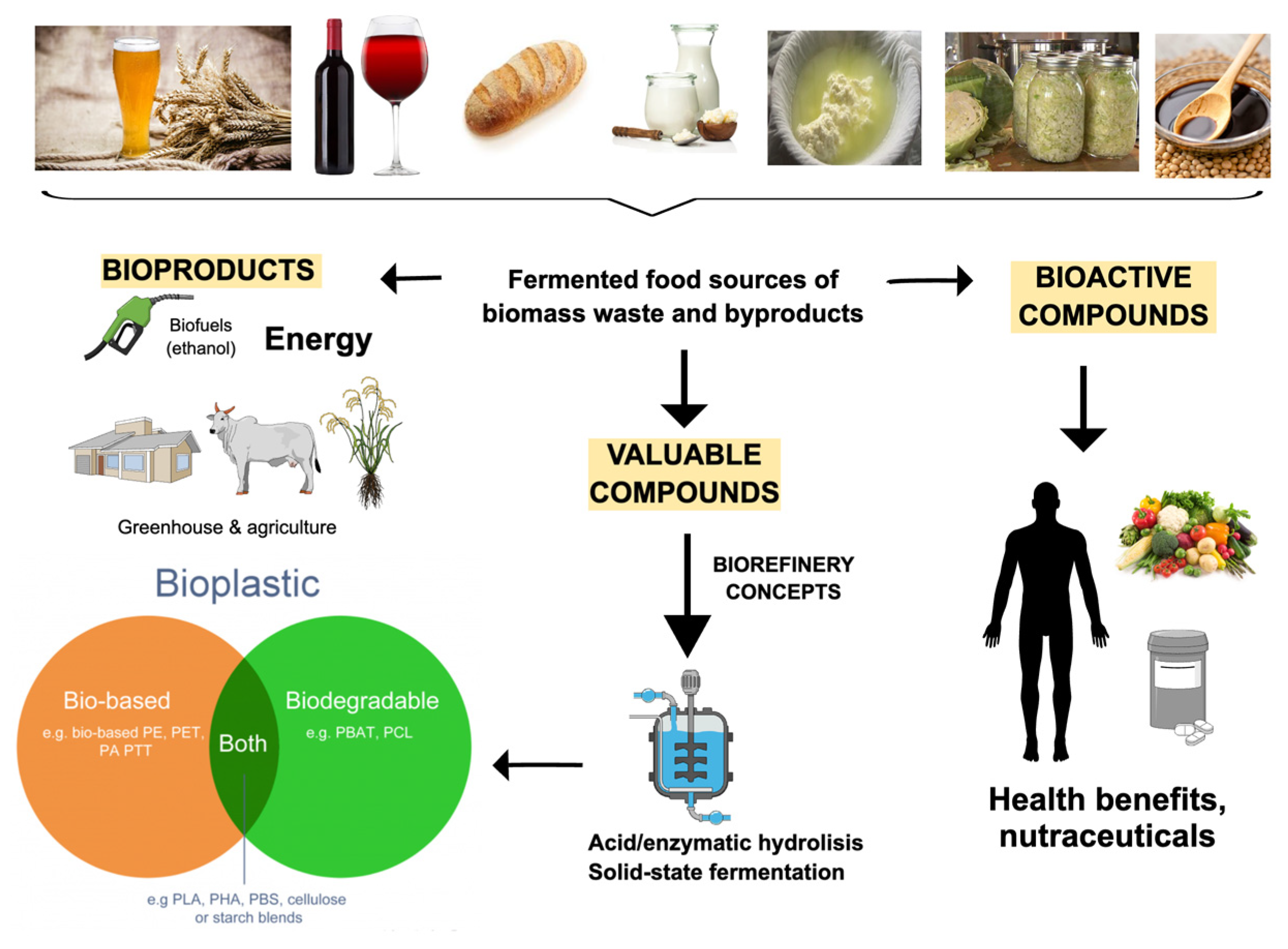
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
7 Factors to Consider When Choosing an HPLC Detector | PerkinElmer Blog
Fermentation | Free Full-Text | Valorization of Fermented Food Wastes and Byproducts: Bioactive and Valuable Compounds, Bioproduct Synthesis, and Applications
Chromatography can be used to separate and identify the components in a mixture. Column chromatography (CC) – a column is packed with a solid and a solvent moves down the column. Gas chromatography (GC) – a column is packed with a solid or with a solid coated by a liquid, and a gas is passed through the column under pressure at high
Application of a Target-Guided Data Processing Approach in Saturated Peak Correction of GC×GC Analysis | Analytical Chemistry UPLC for the Analysis of Synthetic Peptides and for the Development of Isolation Strategies | Waters
Aug 29, 2023Chromatography. Chromatography is a method by which a mixture is separated by distributing its components between two phases. The stationary phase remains fixed in place while the mobile phase carries the components of the mixture through the medium being used. The stationary phase acts as a constraint on many of the components in a mixture